Differential Vs Single-Ended Analog Inputs
This article aims to assist the user with the selection of an Analog input card for their NX system. The NX-AD series of input cards have both a single ended and differential version. The information below will provide an overview on the differences between the two, and general wiring guidelines highlighting compatibility between the possible combinations of sensors and input cards.
Overview
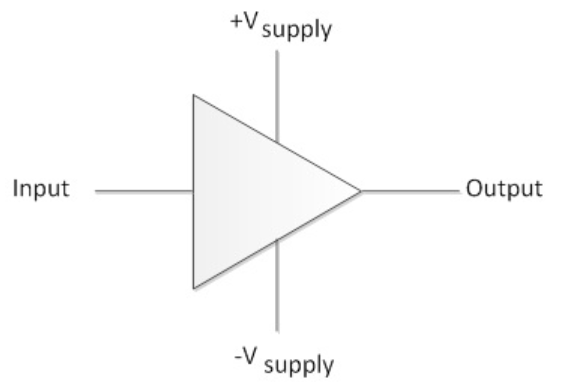
Single Ended Input
A single-ended input, as the name implies, uses a single input signal. The signal is referenced by ground (-). A single-ended input is more sensitive for EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) than his counterpart; the differential input. Another difference between a single-ended and differential is the cable length. The cable length of a single-ended input is considerable shorter compared to a differential input (up to 100 meter) due to the sensitivity of EMI. Below is the schematic overview of a single-ended input.
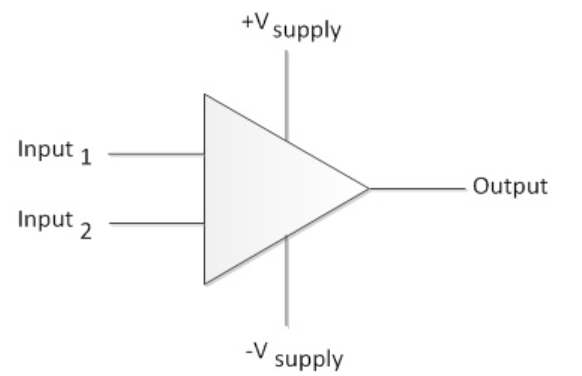
Differential Input
The differential input is slightly different compared to the single-ended input. The differential amplifier uses two input signals instead of a single input. Secondly, the signal is not referenced with ground although it is possible to add ground however this is not common. The advantage by adding ground would be to improve the noise immunity even further.
Instead of a single input the differential input uses two inputs. The differential amplifier amplifies the difference between the two inputs and provides the amplified signal as an output. Below is the schematic overview of a differential input.
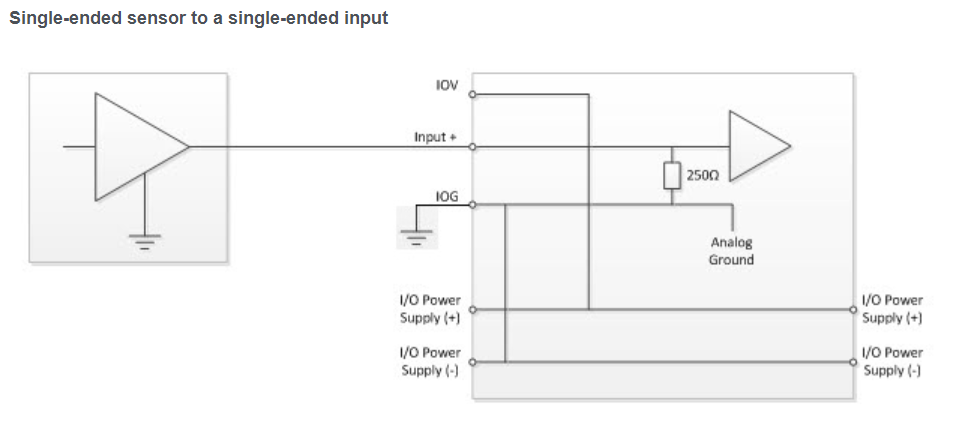
General Wiring Guidelines
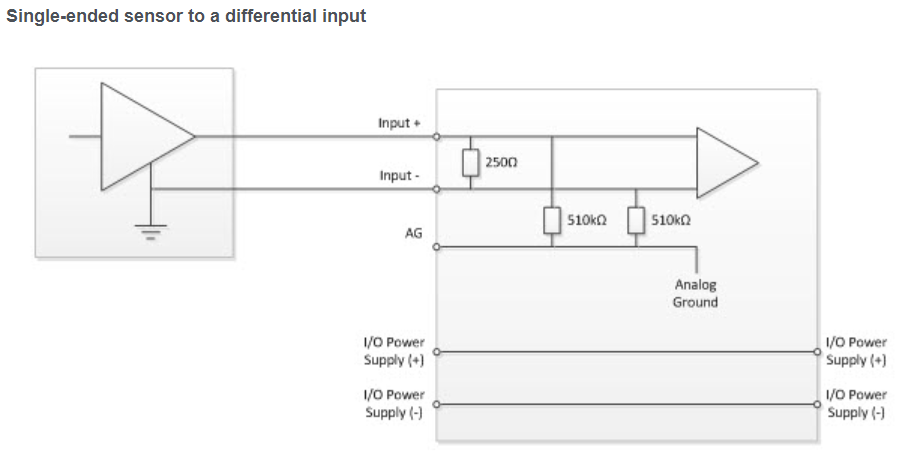
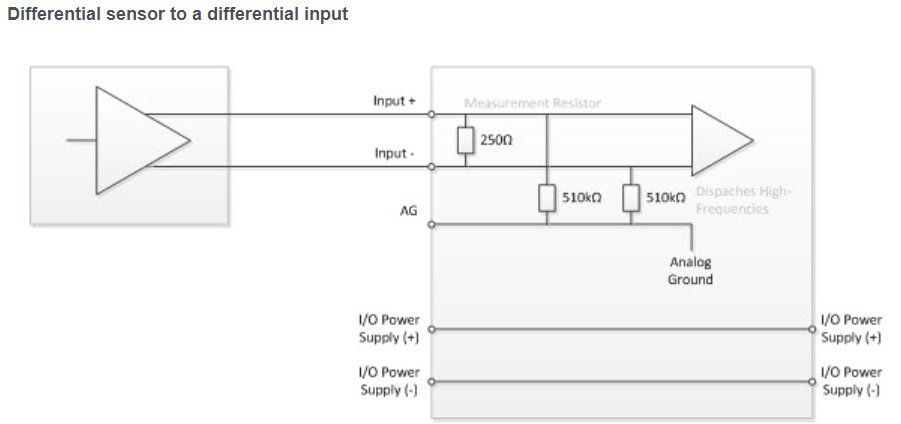

Effects of Noise
In many applications where a signal must be transmitted from one device to another over some distance, external electrical interference (noise) must be considered.
Differential signals provide superior common-mode noise rejection in most cases. The external noise tends to affect both signal wires equally, therefore the difference (potential) between them is normally not disturbed.
A single-ended signal is simpler and less expensive to implement, but also more vulnerable to external noise. There are two sources of erroneous signals with this type of scheme; differences in ground voltage level between transmitting - receiving circuits and the signal wire acts as an antenna to pick up induced noise. Additionally, when there are several signal wires sharing the same "return" ground, this can sometimes cause interference (crosstalk) between the signals.
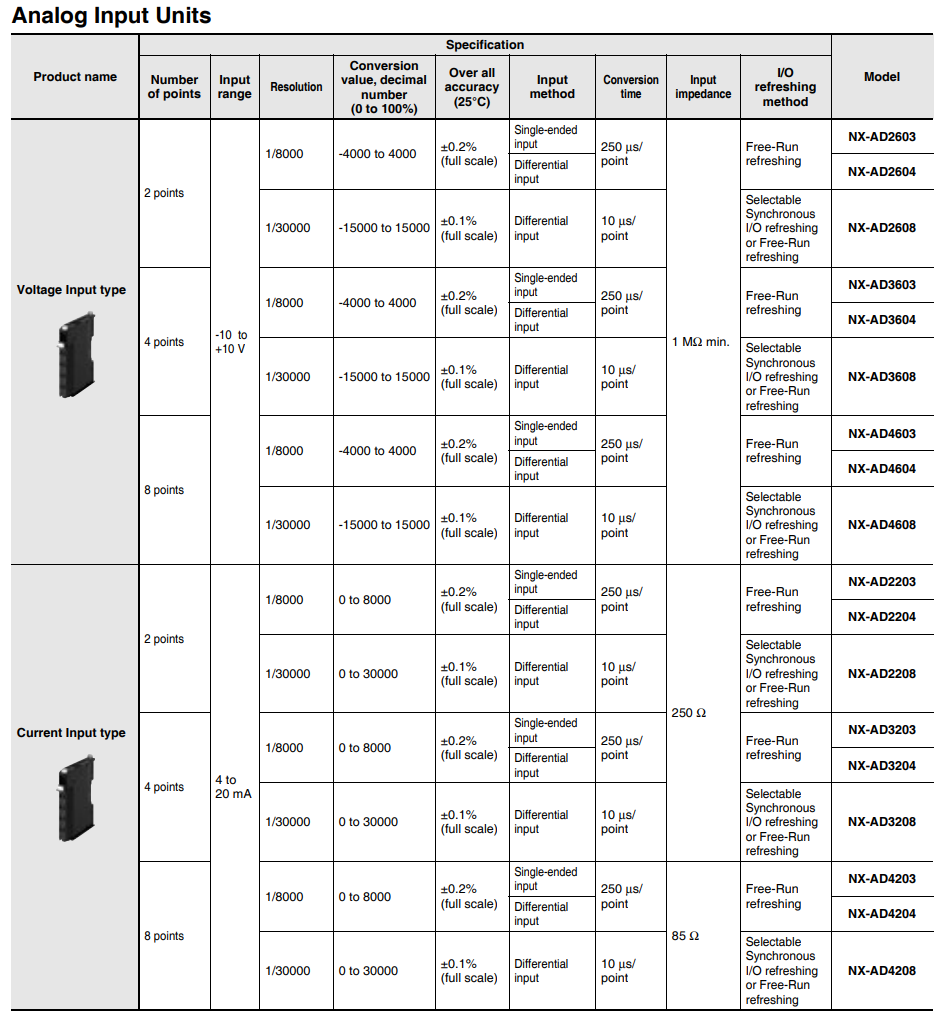
List of Analog Input Cards